Intro to Databases

Putting Things in Context.
Databases allow us to store and perform CRUD actions on data outside of our code therefore allowing our changes to persist to the next session.
ORM Analogy
Where We’re Headed
The Flow
At the end of the phase, we’ll be building out our own API that will sit between our React app and our database, enacting the following data flow:
- React App
- Fetches to API
- API interacts with database and sends response back to the browser/client
- Resolved Promise from fetch leads to change in state
- React updates the DOM
Database Examples
Whats wrong with this table?
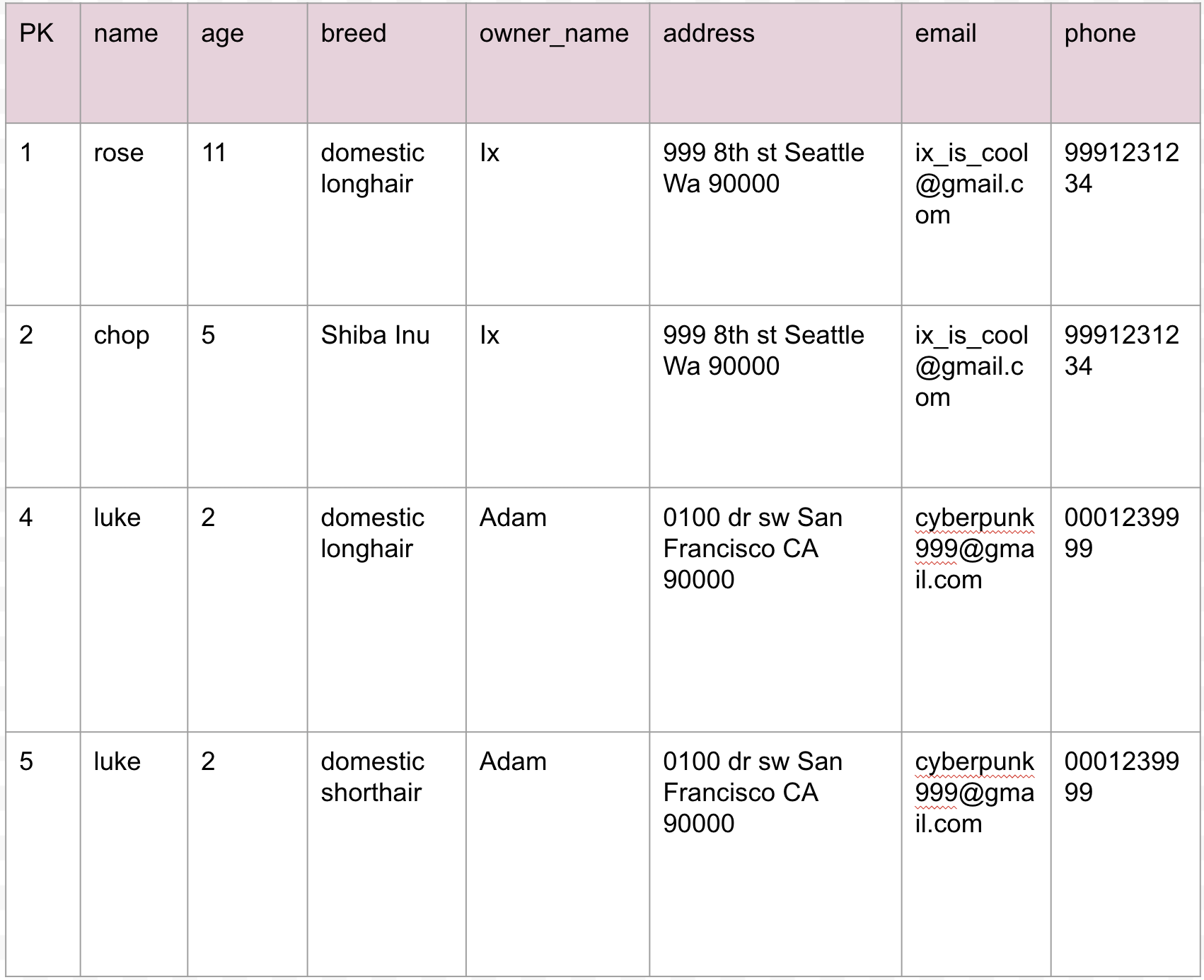
Whats wrong with this table?
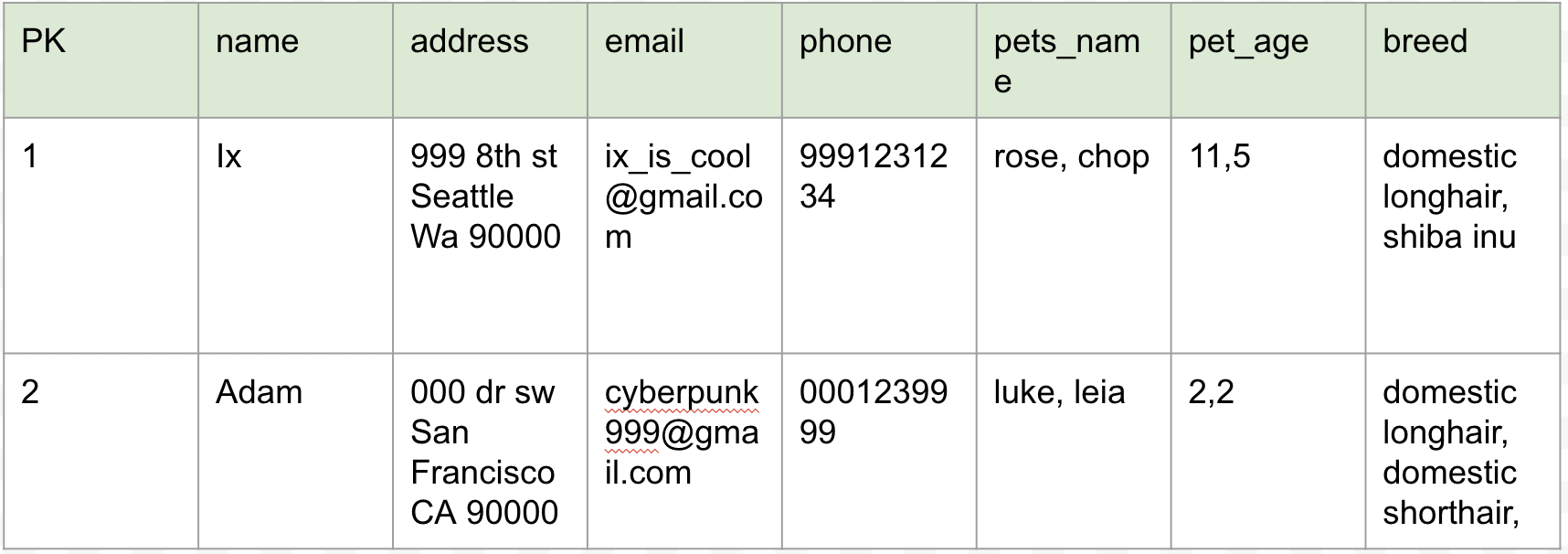
Correct table
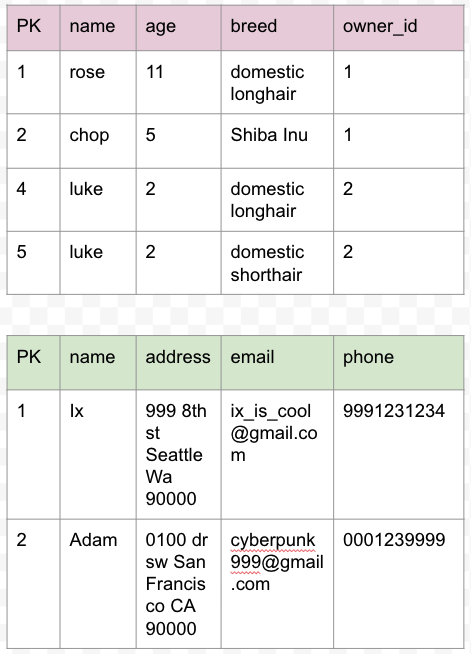
one-to-many
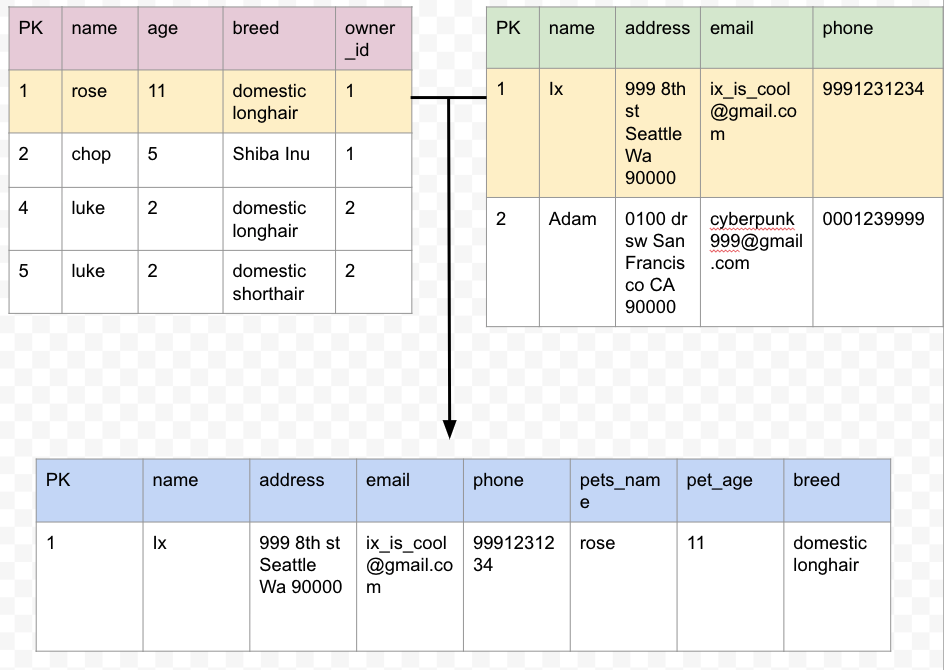
many-to-many
Pet Minder/Rover Clone
Key Features:
- Add persistence
- A Read (SELECT) operation to retrieve persisted pets
- A Create (INSERT INTO) operation to persist new pets
- An Update (UPDATE) operation to update a persisted pet
- An Delete (DELETE) operation to delete a persisted pet
DB Config
Check for prior installation of sqlite
which sqlite3
If not installed, you can install it on MacOS with Homebrew:
brew install sqlite
or for Windows, go to this link
GUI with your SQLite databases
Install DB Browser for SQLite Mac/Windows/Linux
SQLite VSCode Extension OR SQLite Viewer
- WSL Using SQLite with VS Code Extension
- Right click DB and select “Open database”
- In SQLite Explorer, right click the Database and select “New query”
- Write the query, highlight the query, click right and select “Run query”
SQL
SQL(Structured Query Language): A language that allows us to manipulate databases.
SQLite is a library that will allow us to create relational SQL databases.
A relational database is a database of tables and rows with data points that relate to one another. Tables have unique Primary keys and columns that contain data of varying types.
Delete Tables
DROP TABLE dogs;
Create the Tables for pets and owners
CREATE TABLE owners(
id INTEGER PRIMARY KEY,
name TEXT,
address TEXT,
email TEXT,
phone INTEGER
);
CREATE TABLE pets(
id INTEGER PRIMARY KEY,
owner_id INTEGER,
name TEXT,
birthdate INTEGER,
breed TEXT,
favorite_treats TEXT,
last_fed_at DATETIME,
last_walked_at DATETIME,
FOREIGN KEY (owner_id) REFERENCES owners(id)
);
Update Table
ALTER TABLE pets
ADD COLUMN image_url TEXT;
ALTER TABLE pets
RENAME COLUMN birthdate TO age;
Add Data to Table
INSERT INTO owners(name, address, email, phone)
VALUES ('ix', '999 8th st Seattle Wa 90000', 'ix_is_cool@gmail.com', '9991231234');
INSERT INTO owners(name, address, email, phone)
VALUES ('Adam', '000 dr sw San Francisco CA 90000', 'cyberpunk999@gmail.com', '0001239999');
INSERT INTO pets(name, age, breed, favorite_treats, image_url, owner_id)
VALUES ('Luke', '2', 'domestic longhair', 'bacon', 'https://res.cloudinary.com/dnocv6uwb/image/upload/v1631229064/zx6CPsp_d_utkmww.webp', 2);
INSERT INTO pets(name, age, breed, favorite_treats, image_url, owner_id)
VALUES ('rose', '11', 'domestic longhair', 'house plants', 'https://res.cloudinary.com/dnocv6uwb/image/upload/v1631229038/EEE90-E50-25-F0-4-DF0-98-B2-0-E0-B6-F9-BAA89_menwgg.jpg', 1);
INSERT INTO pets(name, age, breed, favorite_treats, image_url, owner_id)
VALUES ('leia', '2', 'domestic Shorthair', 'bacon', 'https://res.cloudinary.com/dnocv6uwb/image/upload/v1631229011/8136c615d670e214f80de4e7fcdf8607--cattle-dogs-mans_vgyqqa.jpg', 2);
INSERT INTO pets(name, age, breed, favorite_treats, image_url, owner_id)
VALUES ('Chop', '5', 'shiba inu', 'cheese', 'https://res.cloudinary.com/dnocv6uwb/image/upload/v1629822267/cdbd77592e3ef91e8cc1cf67d936f94f_fkozjt.jpg', 1);
Query Table Data
SELECT * FROM pets
SELECT * FROM pets
WHERE name = 'rose';
SELECT * FROM pets
WHERE favorite_treats = 'bacon';
SELECT * FROM pets
WHERE age < 5;
UPDATE pets
SET age = 12
WHERE name = 'rose';
UPDATE pets
SET favorite_treats = 'cheese'
DELETE FROM pets WHERE name = 'Chop';
Join Tables
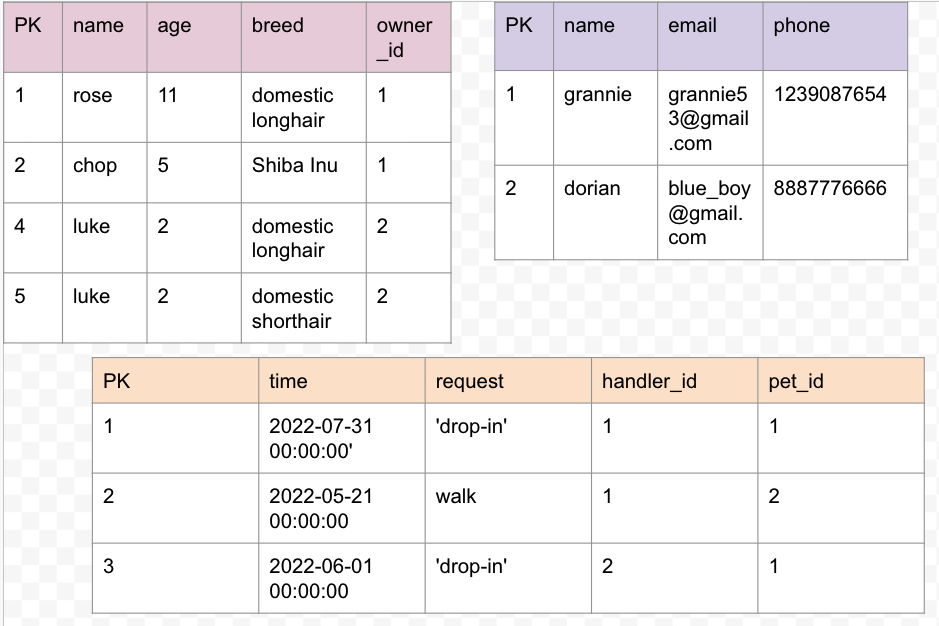
one-to-many
SELECT pets.name, owners.name as 'owner'
FROM pets
JOIN owners ON pets.owner_id = owners.id;
many-to-many
CREATE table
CREATE TABLE handlers(
id INTEGER PRIMARY KEY,
name TEXT,
email TEXT,
phone INTEGER
);
CREATE TABLE jobs(
id INTEGER PRIMARY KEY,
time DATETIME,
request TEXT,
pet_id INTEGER,
handler_id INTEGER,
FOREIGN KEY (handler_id) REFERENCES handlers(id),
FOREIGN KEY (pet_id) REFERENCES pets(id)
);
Create new records
INSERT INTO handlers (name, email, phone)
VALUES ('gannie', 'grannie52@gmail.com', '1239087654');
INSERT INTO handlers (name, email, phone)
VALUES ('dorian', 'blue_boy@gmail.com', '8887776666');
INSERT INTO jobs (time, request, pet_id, handler_id)
VALUES ('2022-07-31 00:00:00', 'drop-in', 1,1);
INSERT INTO jobs (time, request, pet_id, handler_id)
VALUES ('2022-03-01 00:00:00', 'drop-in', 1,1);
INSERT INTO jobs (time, request, pet_id, handler_id)
VALUES ('2022-06-01 00:00:00', 'drop-in', 1,2);
INSERT INTO jobs (time, request, pet_id, handler_id)
VALUES ('2022-05-21 00:00:00', 'walk', 2,2);
READ associated records through joins
SELECT
pets.name,
handlers.name,
jobs.request,
jobs.time
FROM jobs
JOIN pets
ON jobs.pet_id = pets.id
JOIN handlers
ON jobs.handler_id = handlers.id;
SELECT DISTINCT
pets.name,
handlers.name
FROM jobs
JOIN pets
ON jobs.pet_id = pets.id
JOIN handlers
ON jobs.handler_id = handlers.id
AND pets.name = 'Luke';
