Python Data Structures 🏗️

✅ Objectives
- Review the Sequence types:
list,tuple,range(andstr)- Lists: understand CRUD operations with list values
- Tuples:
- Discuss:
mutablevsimmutable - Create and access values in tuples
- Discuss:
- Ranges: and how they’re useful in loops
- Learn about Set types (time permitting)
- Dictionaries:
- a mapping data structure
- know all CRUD operations
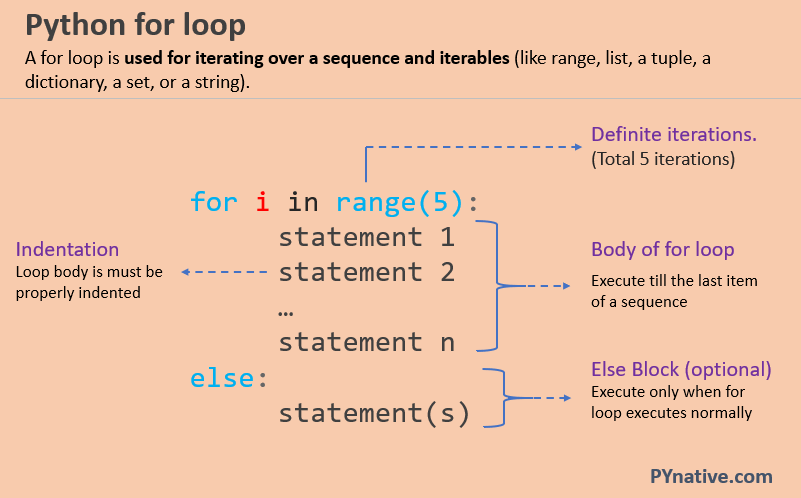
- Loops: create
forandwhileloops with sequences - Use list comprehensions to emulate JS
map,filterandfindfunctions
List... array's Pythonic twin?
- ordered collection of elements
- aka sequence
- mutable
my_list = ["hello", "world", 42, ["another", "list"]]

Let's dive into the code! 🌊
Tuples–when values are forever 💎
- ordered collection of values
- aka sequence
- immutable
my_tuple = (4, 2, "Miyuki", True)
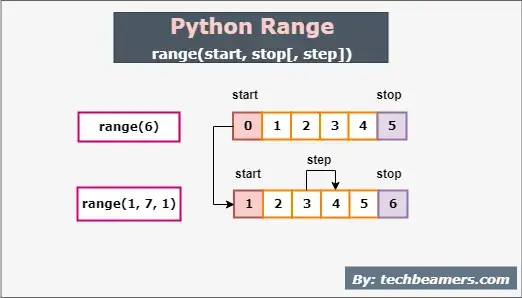
for num in range(8):
print(f"The count is {num}")
Dictionaries 📖 Python's JSON
Creating dictionaries:
cat_1 = { 'name': 'Simon', 'color': 'ginger', 'age': 10 }cat_2 = dict(name='Miyuki', color='grey', age=10)
Reading and adding values 👓
cat_1 = {
'name': 'Simon',
'color': 'ginger',
'age': 10
}
cat_1['color']
# => ginger
cat_1.get('age')
# => 10
cat_1.get('mood')
# => None
cat_1['mood'] = 'hungry'
cat_1.setdefault('breed', 'Munchkin')
Let's try it! 🚀
Updating and Deleting values 📝 ❌
cat_1 = {
'name': 'Simon',
'color': 'ginger',
'age': 10,
'mood': 'hungry'
}
cat_1['mood'] = 'sleepy'
cat_1.update(age=11, mood='feisty')
print(cat_1)
# {'name': 'Simon', 'color': 'ginger', 'age': 11, 'mood': 'feisty'}
del cat_1('age')
cat_1.pop('mood')
print(cat_1)
# {'name': 'Simon', 'color': 'ginger'}
Let's do it! 🛠️
For loops: let me reiterate 🐈🐈🐈
break keyword 🔑
In a loop, the
break keyword escapes the loop, regardless of the iteration number. Once break executes, the program will continue to execute after the loop.
numbers = [0, 254, 2, -1, 3]
for num in numbers:
if (num < 0):
print("Negative number detected!")
break
print(num)
# 0
# 254
# 2
# Negative number detected!
continue keyword 🔑
In Python, a
while loop will repeatedly execute a code block as long as a condition evaluates to True.
big_number_list = [1, 2, -1, 4, -5, 5, 2, -9]
# Print only positive numbers:
for i in big_number_list:
if i < 0:
continue
print(i)
while loops 🔍
In Python, the
continue keyword is used inside a loop to skip the remaining code inside the loop code block and begin the next loop iteration.
hunger = 5
while hunger > 0:
print('munch!')
hunger -= 1 # be sure to progress your condition towards the base case!
# this will print 'munch!' 5 times
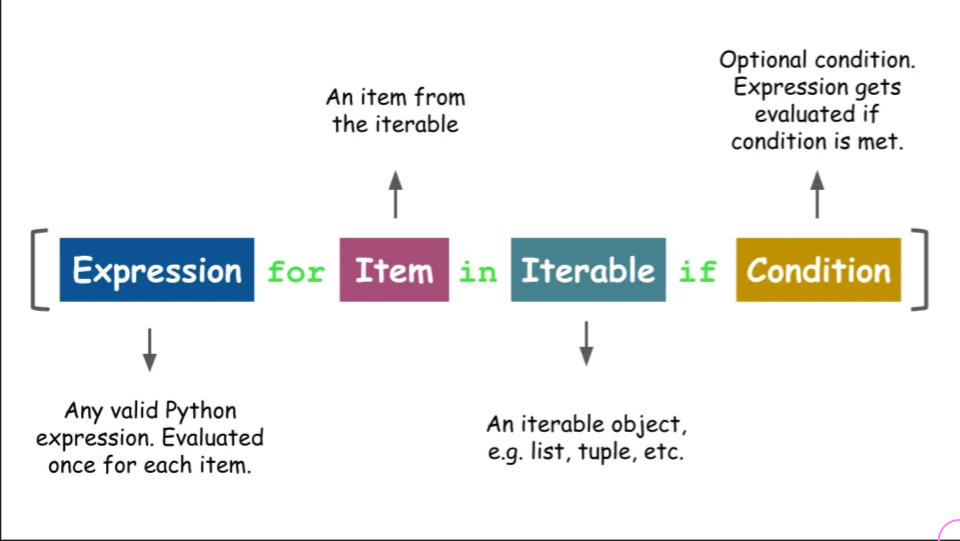
List Comprehension 💡
List comprehension is a simpler method to create a list from an existing list. It is generally a list of iterables generated with an option to include only the items which satisfy a condition.