Transport Protocols
The VISSv3.0 specification lists the transport protocols HTTP, WebSocket, gRPC, and MQTT as supported.
However, this is not necessarily a final list as says that any protocol that transport the primary payloads of this specification,
or an encoded version of the primary payloads, can be included on this list.
The specification does not mandate the use of a specific transport protocol,
but at least one of the listed transport protocols MUST be supported.
Secure WebSocket
The WebSocket protocol is used in this document to provide examples of a protocol that does not apply any deviations to the primary payload format.
As it does not implicitly provide a logical association between the request and response messages,
a key-value pair with the key name "requestId" MUST be added to the data components, as described in the [[CORE]] specification.
Additionally, since WebSocket does not define explicit methods, another key-value pair, "action", MUST also be included.
Refer to the for detailed descriptions of these key-value pairs.
All data components are mapped to the payload.
Session Life Time Management
Initialization
If the client application is an HTML Application running in a web runtime or is a web page running in a browser, the WebSocket instance may either be instantiated natively or be created using a 'standards compliant' WebSocket JavaScript library.
A WebSocket can also be initiated from a native application (e.g., written in C++) or from a managed runtime environment such as Java or C#. In these cases, it is assumed that the client uses a standards-compliant WebSocket library to request a connection with the server.
Implementations that support additional devices or multiple VISSv3 services should provide discovery. Alternatively, the location of a particular VISSv3 Server instance on the local vehicle network may be handled by configuration, either as part of a package manifest or by consulting a registry on application install. The 'wwwVISSv3' hostname in this specification is used an example.
A client running on the vehicle is able to connect to the VISSv3 Server instance using the hostname e.g. 'wwwVISSv3' and uses the default port 6443. The hostname 'wwwVISSv3' may locally be mapped to the localhost IP address 127.0.0.1 e.g. by adding an entry to the /etc/hosts file.
The sub-protocol name SHALL be 'VISSv3' with the digit 3 being the version number. The sub-protocol version will be associated with exactly one VISS Server Specification version so that the client and server can correctly validate and parse request and response message packets.
var vehicle = new WebSocket("wss://wwwVISSv3:6443", "VISSv3");
The client SHALL connect to the server over HTTPS and request that the server opens a WebSocket. All WebSocket communications between the client and server MUST use ‘wss’ (WebSocket Secure). Non encrypted communication is not supported, hence the server MUST reject ‘ws’ connection requests.
This specification assumes that a single WebSocket is used to enable communication between a client application and the server. The client MAY open more than one websocket. However, the server MAY reject to open a subsequent WebSocket connection and the client is responsible for handling this gracefully.
If multiple WebSocket connection is established between a client application and the server then each connection MUST be managed independently. For example, subscriptions created through one connection can only trigger events through that same connection, and the client MUST use the same connection to unsubscribe.
If multiple WebSocket connection has been established between one or more clients and a particular server instance, there is a risk that race conditions and concurrency issues could occur. For instance, simultaneous updates to the same signal from different connections could result in conflicts.
Unless explicitly stated otherwise, the client MAY assume that the server implements a basic concurrency model, meaning that lost updates or dirty reads could occur when multiple WebSocket connections are in use.
Closure
The WebSocket connection MAY be closed by either the client or the server by invoking the ‘close()’ method on the WebSocket instance.
The following example shows the typical lifecycle of a WebSocket connection on the client side:
// Open the WebSocket
var vehicle = new WebSocket("wss://wwwVISSv3:6443", "VISSv3");
…
// Close the WebSocket
vehicle.close();
The VISSv3 server MAY also terminate the connection if it does not receive any requests from the client within a server-defined timeout period. In such cases, the client MUST handle the closure gracefully, and if needed, re-establish the connection and request new subscriptions, where required.
Transport Messages
Read
The client MAY send a getRequest message to the server to get the value of one or more vehicle signals. If the server can fulfill the request, it SHALL return a getSuccessResponse message. If an error occurs, the server SHALL return a getErrorResponse message. The structure of these message objects is defined in the tables below:
| Object Name | Attribute | Type | Required |
|---|---|---|---|
| getRequest | action | Action | Yes |
| path | string | Yes | |
| filter | string | Optional | |
| authorization | string | Optional | |
| data compression | string | Optional | |
| requestId | string | Yes |
| Object Name | Attribute | Type | Required |
|---|---|---|---|
| getSuccessResponse | action | Action | Yes |
| requestId | string | Yes | |
| data | object/array | Yes | |
| ts | string | Yes |
In the table above, the "data" attribute is either an object containing "value" and "ts" name/value pairs, or an array of such objects.
| Object Name | Attribute | Type | Required |
|---|---|---|---|
| getErrorResponse | action | Action | Yes |
| requestId | string | Yes | |
| error | Error | Yes | |
| ts | string | Yes |
Example:
Request:
{
"action": "get",
"path": "Vehicle.Powertrain.CombustionEngine.RPM",
"requestId": "8756"
}
{
"action": "get",
"requestId": "8756",
"data":{"path":"Vehicle.Powertrain.CombustionEngine.RPM",
"dp":{"value":"2372", "ts":"2020-04-15T13:37:00Z"}
},
"ts":"2020-04-15T13:37:05Z"
}
{
"action": "get",
"requestId": "8756",
"error": {"number": "404", "reason": "unavailable_data", "description": "The requested data was not found."},
"ts": "2020-04-15T13:37:00Z"
}
Search Read
The client MAY issue a search read request to retrieve multiple signal values in one request message. This is realized by adding a "filter" object following the section 7.1 Paths Filter Operation described in the [[CORE]] specification.
Example:
Request:
{
"action": "get",
"path": "Vehicle.Cabin",
"filter": {"variant":"paths", "parameter":["Door.*.*.IsOpen", "DriverPosition"]},
"requestId": "5688"
}
{
"action": "get",
"data":[{"path":"Vehicle.Cabin.Door.Row1.Left.IsOpen", "dp":{"value":"false", "ts":"2020-04-15T13:37:00Z"}},
{...},…
{"path":"Vehicle.Cabin.Door.Row4.Right.IsOpen", "dp":{"value":"true", "ts":"2020-04-15T13:37:01Z"}},
{"path":"Vehicle.Cabin.DriverPosition", "dp":{"value":"1", "ts":"2020-04-15T07:00:01Z"}}
],
"requestId": "5688",
"ts":"2020-04-15T07:00:02Z"
}
History Read
A client MAY issue a history read request to retrieve previously recorded data points. This is realized by adding a "filter" object following the section 7.2 History Filter Operation described in the [[CORE]] specification.
Example:
Request:
{
"action": "get",
"path": "Vehicle.Acceleration.Longitudinal",
"filter": {"variant":"history", "parameter":"P2DT12H"},
"requestId": "5688"
}
{
"action": "get",
"data": {"path": "Vehicle.Acceleration.Longitudinal", "dp": [{"value": "0.123", "ts": "2020-04-15T13:00:00Z"}, {"value": "0.125", "ts": "2020-04-15T13:37:02Z"}]},
"requestId": "5688",
"ts": "2020-04-15T13:37:02Z"
}
Signal Discovery Read
To retrieve metadata about the VSS tree, the client MAY issue a signal discovery read request. This is realized by adding a "filter" object following the section 7.7 Metadata Filter Operation described in the [[CORE]] specification. The response includes metadata for all nodes in the subtree rooted at the node specified by the path, limited to the number of generations set by the "parameter" value.
Example:
Request:
{
"action": "get",
"path": "Vehicle.Powertrain.FuelSystem",
"filter":{"variant":"metadata", "parameter":"2"},
"requestId": "5687"
}
{
"action": "get",
"requestId": "5687",
"metadata": {"FuelSystem":{"type":"branch","children":["HybridType", ... ]}},
"ts": "2020-04-15T13:37:00Z"
}
Update
The client MAY send a request to the server to set the value of a signal. If the server can fulfill the request successfully, it SHALL return a setSuccessResponse message. If an error occurs, the server SHALL return a setErrorResponse message. The structure of these message objects is defined below:
| Object Name | Attribute | Type | Required |
|---|---|---|---|
| setRequest | action | Action | Yes |
| path | string | Yes | |
| value | string/array/object | Yes | |
| authorization | string | Optional | |
| requestId | string | Yes |
| Object Name | Attribute | Type | Required |
|---|---|---|---|
| setSuccessResponse | action | Action | Yes |
| requestId | string | Yes | |
| ts | string | Yes |
| Object Name | Attribute | Type | Required |
|---|---|---|---|
| setErrorResponse | action | Action | Yes |
| requestId | string | Yes | |
| error | Error | Yes | |
| ts | string | Yes |
Example:
Request:
{
"action": "set",
"path": "Vehicle.Powertrain.Transmission.PerformanceMode",
"value": "sport",
"requestId": "5687"
}
{
"action": "set",
"requestId": "5687",
"ts": "2020-04-15T13:37:00Z"
}
{
"action": "set",
"requestId": "5687",
"error": {"number": "404", "reason": "unavailable_data", "description": "The requested data was not found."},
"ts": "2020-04-15T13:37:00Z"
}
Subscribe
The client MAY send a subscribeRequest message
to request a subscription to one or more signals,
thereby requesting the server to repeatedly return subscription event messages based on
the section 7. Filter Request described in the [[CORE]] specification.
To reduce processing load, the server MAY limit the number of
subcriptionEvent messages sent.
If the server can fulfill the request, it SHALL return a
subscribeSuccessResponse message.
If an error occurs while processing the request, the server SHALL return a
subscribeErrorResponse message.
If an error occurs during an active subscription session, the server SHALL return a
subscriptionErrorEvent message.
The structure of the subscription messages is defined below.
As specified in the [[CORE]] specification, the supported subscription variants are:
- timebased: Event messages are issued at a regular time interval,
- change: Event messages are issued when the value has changed as specified,
- range: Event messages are issued when the value is in the specified range,
- curvelog: Event messages are issued when the buffer is full, and then processed according to the curve logging algorithm.
| Object Name | Attribute | Type | Required |
|---|---|---|---|
| subscribeRequest | action | Action | Yes |
| path | string | Yes | |
| filter | string | Yes | |
| authorization | string | Optional | |
| data compression | string | Optional | |
| requestId | string | Yes |
| Object Name | Attribute | Type | Required |
|---|---|---|---|
| subscribeSuccessResponse | action | Action | Yes |
| requestId | string | Yes | |
| subscriptionId | string | Yes | |
| ts | string | Yes |
| Object Name | Attribute | Type | Required |
|---|---|---|---|
| subscribeErrorResponse | action | Action | Yes |
| requestId | string | Yes | |
| error | Error | Yes | |
| ts | string | Yes |
| Object Name | Attribute | Type | Required |
|---|---|---|---|
| subscriptionEvent | action | Action | Yes |
| subscriptionId | string | Yes | |
| data | object/array | Yes | |
| ts | string | Yes |
| Object Name | Attribute | Type | Required |
|---|---|---|---|
| subscriptionErrorEvent | action | Action | Yes |
| subscriptionId | string | Yes | |
| error | Error | Yes | |
| ts | string | Yes |
Example:
Request:
{
"action": "subscribe",
"path": "Vehicle.Powertrain.FuelSystem.Level",
"filter": {"variant":"timebased", "parameter":{"period":"500"}},
"requestId": "6578"
}
{
"action": "subscribe",
"subscriptionId": "12345",
"requestId": "6578",
"ts": "2020-04-15T13:37:00Z"
}
{
"action": "subscribe",
"requestId": "6578",
"error": {"number": "404", "reason": "unavailable_data", "description": "The requested data was not found."},
"ts": "2020-04-15T13:37:00Z"
}
{
"action": "subscription",
"subscriptionId": "12345",
"data": {"path": "Vehicle.Powertrain.FuelSystem.Level",
"dp": {"value": "50", "ts": "2020-04-15T13:37:00Z"}
},
"ts": "2020-04-15T13:37:00Z"
}
{
"action": "subscription",
"subscriptionId": "12345",
"error": {"number": "401", "reason": "expired_token", "description": "Access token has expired."},
"ts": "2020-04-15T13:37:00Z"
}
Curve Logging Subscribe
Curve logging data compression by eliminating data points that are within a set error margin is activated via a subscription request. Event messages will be issued when the buffer becomes full, after insignificant data points have been eliminated, refer to the section 7.6 Curve logging Filter Operation in the [[CORE]] specification.
Example:
Request:
{
"action": "subscribe",
"path": "Vehicle.Powertrain.FuelSystem.Level",
"filter": {"variant":"curvelog", "parameter":{"maxerr":"0.5", "bufsize":"100"}},
"requestId": "6578"
}
{
"action": "subscribe",
"subscriptionId": "12345",
"requestId": "6578",
"ts": "2020-04-15T13:37:00Z"
}
{
"action": "subscription",
"subscriptionId": "12345",
"data":{"path": "Vehicle.Powertrain.FuelSystem.Level",
"dp":[{"value": "50", "ts": "2020-04-15T13:38:00Z"}, ..., {"value": "25", "ts": "2020-04-15T13:39:30Z"}]
},
"ts": "2020-04-15T13:37:00Z"
}
Range Subscribe
Subscription to a range of values, that can have either a single boundary, or multipe boundaries as in the example below. For a more information how to use range of values, refer to the section 7.4 Range Filter Operation in the [[CORE]] specification.
Example:
Request:
{
"action": "subscribe",
"path": "Vehicle.Powertrain.FuelSystem.Level",
"filter": "filter":{"variant":"range","parameter":[{"logic-op":"lt","boundary":"50","combination-op":"OR"},{"logic-op":"gt","boundary":"55"}]},
"requestId": "6578"
}
{
"action": "subscribe",
"subscriptionId": "12345",
"requestId": "6578",
"ts": "2020-04-15T13:37:00Z"
}
{
"action": "subscription",
"subscriptionId": "12345",
"data":{"path": "Vehicle.Powertrain.FuelSystem.Level",
"dp":{"value": "51", "ts": "2020-04-15T14:00:00Z"}},
"ts": "2020-04-15T14:00:00Z"
}
Change Subscribe
Subscription to when a signal has changed between two sequential captures. For a more information how to use change of values, refer to the section 7.5 Change Filter Operation in the [[CORE]] specification.
Example:
Request:
{
"action": "subscribe",
"path": "Vehicle.Powertrain.FuelSystem.Level",
"filter":{"variant":"change","parameter":{"logic-op":"gt","diff":"10"}},
"requestId": "6578"
}
{
"action": "subscribe",
"subscriptionId": "12345",
"requestId": "6578",
"ts": "2020-04-15T13:37:00Z"
}
{
"action": "subscription",
"subscriptionId": "12345",
"data":{"path": "Vehicle.Powertrain.FuelSystem.Level",
"dp":{"value": "101", "ts": "2020-04-15T14:00:00Z"}},
"ts": "2020-04-15T14:00:00Z"
}
Unsubscribe
To unsubscribe from a subscription, the client SHALL send an
unsubscribeRequest message to the server.
If the server can fulfill the request successfully, it SHALL returns an
unsubscribeSuccessResponse message.
If an error occurs, an
unsubscribeErrorResponse message SHALL be returned.
If the client has created multiple WebSocket instance, it MUST unsubscribe
using the same WebSocket instance that was originally used to create the subscription.
| Object Name | Attribute | Type | Required |
|---|---|---|---|
| unsubscribeRequest | action | Action | Yes |
| subscriptionId | string | Yes | |
| requestId | string | Yes |
| Object Name | Attribute | Type | Required |
|---|---|---|---|
| unsubscribeSuccessResponse | action | Action | Yes |
| requestId | string | Yes | |
| ts | string | Yes |
| Object Name | Attribute | Type | Required |
|---|---|---|---|
| unsubscribeErrorResponse | action | Action | Yes |
| requestId | string | Yes | |
| error | Error | Yes | |
| ts | string | Yes |
Example:
Request:
{
"action": "unsubscribe",
"subscriptionId": "12345",
"requestId": "5786"
}
{
"action": "unsubscribe",
"requestId": "5786",
"ts": "2020-04-15T13:37:00Z"
}
{
"action": "unsubscribe",
"requestId": "6578",
"error": {"number": "400", "reason": "invalid_data", "description": "Data present in the request is invalid."},
"ts": "2020-04-15T13:37:00Z"
}
HTTPS
The message data components described in the [[CORE]] specification are primarily mapped to standard HTTP parameters. Only when no suitable mapping is available are they included in the payload. The most significant deviations are as follows:
- The path is included as part of the URL.
- A filter expression is added to the URL as a query string.
- The HTTP methods GET and POST are used instead of the "action" field.
Session Life Time Management
Initialization
Initialization involves setting up a secure HTTPS session between the client and the server.
This ensures encrypted communication for data transmission.
To initialize a secure session, the client sends a request to the server using the HTTPS protocol.
This is achieved by connecting to the server's designated URL using the 'https://' scheme.
The client can use a web browser, a native application, or a suitable library in the case of programmatically managed sessions.
While the client typically connects to the server using the specified hostname, which often includes the "www" prefix,
it's important to note that this convention may not apply in situations where VISS operates within a local, in-vehicle network or if remote vehicle connections are allowed.
The communication SHALL use port 443, the default port for secure HTTPS connections.
Hostname resolution can be achieved using DNS or configured through local settings.
Closure
Closure entails ending the established HTTPS session when the communication is complete or when the client no longer requires the connection.
Either the client or the server can initiate the session closure. The client can signal the end of the session by sending an appropriate request to the server,
indicating the intent to close the connection.
Upon session closure, any allocated resources, such as server-side threads or memory, are released, improving overall system efficiency.
Transport Messages
Read
The client MAY send a HTTPS GET request message to the server to get one or more value(s) of one or more vehicle signal(s). If the server can fulfill the request, it SHALL return a response containing the requested value(s). If the server is unable to fulfill the request, e.g. because the client is not authorized to retrieve one or more of the signals, then it SHALL respond with an appropriate error status code.
Example: Request:
GET /Vehicle/Cabin/SeatPosCount HTTP/1.1
Host: 127.0.0.1:1337
Accept: application/json
...
HTTP/1.1 200 OK
Content-Type: application/json; charset=utf-8
...
{
"data":{"path":"Vehicle.Cabin.SeatPosCount",
"dp":{"value":["2", "3", "2"], "ts":"2020-04-15T13:37:00Z"}
},
"ts": "2020-04-15T13:37:00Z"
}
HTTP/1.1 404 Not Found
Content-Type: application/json; charset=utf-8
...
{
"error": {"number": "404", "reason": "unavailable_data", "description": "The requested data was not found."},
"ts": "2020-04-15T13:37:00Z"
}
Search Read
The search read request uses the section 7.1 Paths Filter Operation
described in the [[CORE]] specification to define one or more path expressions, relative to the path in the GET URL.
Example:
Request:
GET /Vehicle/Cabin/Door?filter={"variant":"paths", "parameter":"*/*/IsOpen"} HTTP/1.1
Host: 127.0.0.1:1337
Accept: application/json
...
HTTP/1.1 200 OK
Content-Type: application/json; charset=utf-8
...
{
"data":[{"path":"Vehicle.Cabin.Door.Row1.Left.IsOpen", "dp":{"value":"false", "ts":"2020-04-15T13:37:00Z"}},
{...},…
{"path":"Vehicle.Cabin.Door.Row4.Right.IsOpen", "dp":{"value":"true", "ts":"2020-04-15T13:37:00Z"}}
],
"ts": "2020-04-15T13:37:00Z"
}
HTTP/1.1 404 Not Found
Content-Type: application/json; charset=utf-8
...
{
"error": {"number": "404", "reason": "unavailable_data", "description": "The requested data was not found."},
"ts": "2020-04-15T13:37:00Z"
}
History Read
The history read request uses the section 7.2 History Filter Operation
described in the [[CORE]] specification to read recorded values
for a specific past duration.
Example:
Request:
GET /Vehicle.Acceleration.Longitudinal?filter={"variant":"history", "parameter":"P2DT12H"} HTTP/1.1
Host: 127.0.0.1:1337
Accept: application/json
...
HTTP/1.1 200 OK
Content-Type: application/json; charset=utf-8
...
{
"data":{"path":"Vehicle.Acceleration.Longitudinal", "dp":[{"value":"0.123", "ts":"2020-04-15T13:00:00Z"}, ..., {"value":"0.125", "ts":"2020-04-15T13:37:00Z"}]},
"ts": "2020-04-15T13:37:00Z"
}
Signal Discovery Read
The signal discovery request uses the section 7.7 Metadata Filter Operation
described in the [[CORE]] specification to retrieve metadata from a specified subtree in the VSS tree.
A successful response will contain the requested metadata from all nodes of the subtree defined by
the subtree root node addressed by the path.
The depth of metadata retrieval is controlled by the "parameter" value.
Example:
Request:
GET /Vehicle/Powertrain/FuelSystem?filter={"variant":"metadata", "parameter":"0"} HTTP/1.1
Host: 127.0.0.1:1337
Accept: application/json
...
HTTP/1.1 200 OK
Content-Type: application/json; charset=utf-8
...
{
"metadata": {"FuelSystem":{"type":"branch","description":"Fuel system data.","children":{"HybridType, ... }}},
"ts": "2020-04-15T13:37:00Z"
}
Update
The client MAY send a request to update the value of a signal. If the server can fulfill the request, it SHALL return a setSuccessResponse message. If an error occurs, e.g. because the client is not authorized to set the requested value, or the value is read-only, the server SHALL return a setErrorResponse message.
Example:
POST /Vehicle/Powertrain/Transmission/PerformanceMode HTTP/1.1
Host: 127.0.0.1:1337
Accept: application/json
...
{
"value": "sport"
}
HTTP/1.1 200 OK
Content-Type: application/json; charset=utf-8
...
{
"ts": "2020-04-15T13:37:00Z"
}
HTTP/1.1 404 Not Found
Content-Type: application/json; charset=utf-8
...
{
"error": {"number": "404", "reason": "unavailable_data", "description": "The requested data was not found."},
"ts": "2020-04-15T13:37:00Z"
}
MQTT
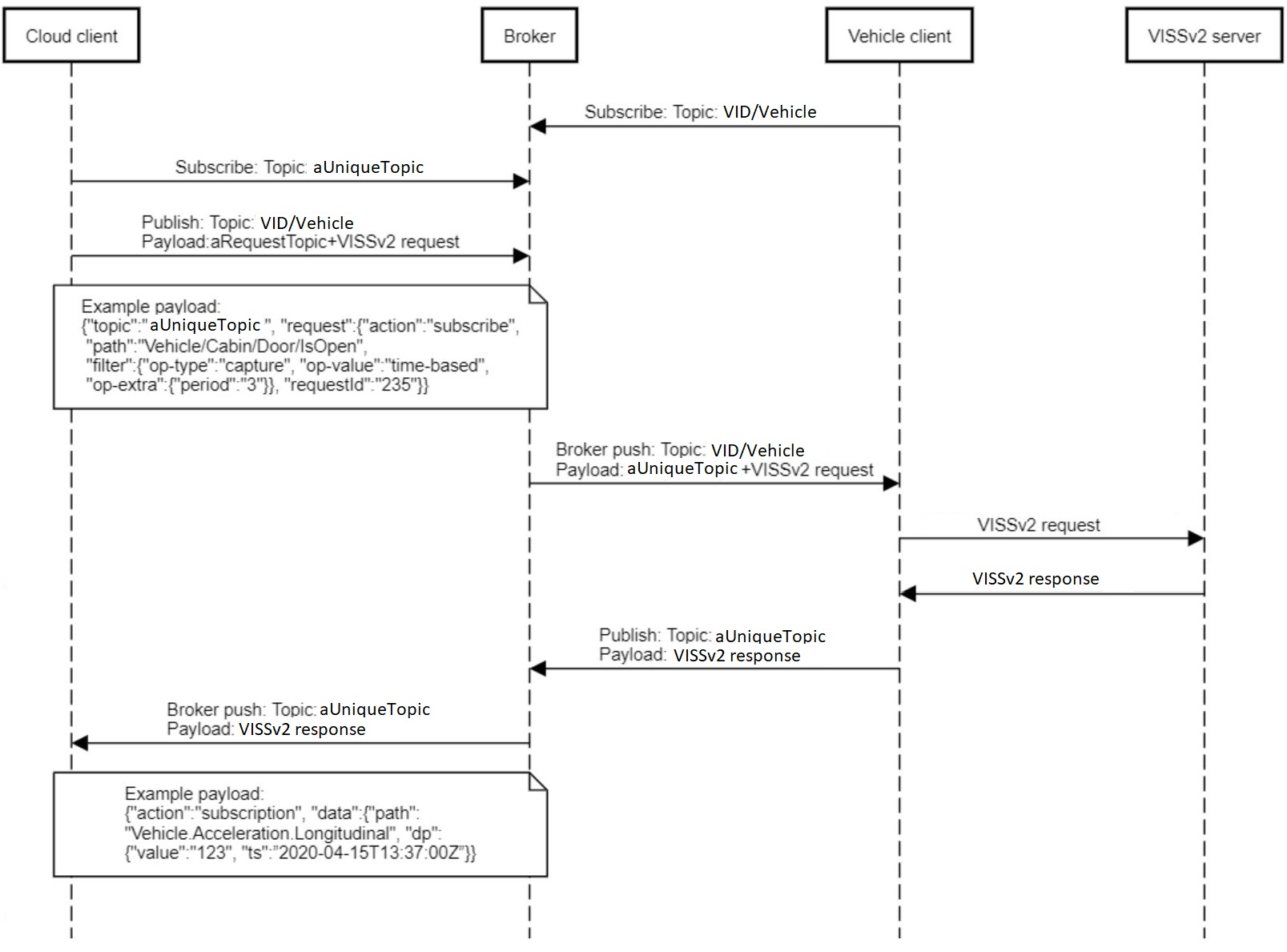
The MQTT protocol operates on a publish-subscribe communication model, whereas the VISS is designed around a client-server interaction model.
To reconcile these differences, a lightweight application-level protocol is introduced on top of MQTT.
This protocol encapsulates VISS messages within MQTT messages and includes additional metadata required to support client-server semantics.
Details of this abstraction mechanism are provided in the following sections.
The VISS messages transmitted over MQTT SHALL conform to the primary payload format without modification.
Application Level Protocol
For MQTT to support the full VISSv3 interface, as decribed in the section 5. Interface of the [[CORE]] specification,
an application-level protocol that runs on top of MQTT is required.
This protocol is described below and illustrated in the accompanying sequence diagram.
To emulate the client-server pattern that is described in the [[CORE]] specification,
the vehicle server—via its vehicle-side client—MUST subscribe to the broker on a topic named VID/Vehicle,
where VID represents a unique identifier that links the vehicle to the access control ecosystem.
This vehicle identifier is not necessarily the manufacturer's Vehicle Identification Number (VIN).
The cloud-side client is expected to have access to this vehicle identifier.
How it obtains it is out of scope for this specification.
When the cloud client intends to send a request to the vehicle server,
it first generates a unique topic name and subscribes to it via the broker.
The client then generates a JSON formatted payload with the following structure:
{"topic":"aUniqueTopic", "request":"VISSv3Request"}
For subscription requests, the vehicle client MUST store the subscriptionId from the subscribe response, together with the topic name associated to the subscribe request. When the vehicle server later issues event messages, the vehicle client SHALL extract the subscriptionId from it, and retrieve the topic name associated to it. The vehicle client SHALL delete the saved topic name and subscriptionId when it receives an unsubscribe request in a message from the broker.
In subsequent requests from the cloud client, the unique topic name MAY be reused from the previous request-response cycle, or a new unique topic name MAY be generated. If a new topic name is used, the previous one SHOULD be unsubscribed. The vehicle client MAY continue using the topic name to which it initially subscribed.
The payload format of all response and event messages SHALL conform to the primary payload format defined in this specification. The access control model is also applicable to this transport mechanism. The Access Token Server SHOULD implement its own version of the application-level protocol described here, using the topic name "VID/ATS". Similarly, the Access Grant Token Server MAY implement the same mechanism using the topic "VID/AGTS", or if it is deployed in the cloud it MAY expose the HTTPS interface defined in this specification.
Security Aspects
The MQTT architecture requires the use of a broker, which serves as an intermediary between the client and server endpoints (referred to as the subscriber and publisher in MQTT terminology). Since each TLS channel terminates at the broker, it has full access to all plaintext communication between these endpoints. This security consideration SHALL be taken into account when selecting MQTT as a transport protocol.
Transport Messages
As described in the "Application Level Protocol" section, each request message sent to the broker SHALL include two JSON-formatted key-value pairs. The value of the request key MUST be a string containing the client request intended for the vehicle server. This request MUST strictly adhere to the primary payload format defined in this specification.
gRPC
The gRPC protocol uses Protocol Buffers (Protobuf) for message serialization. The Protobuf message definitions SHALL be specified in a .proto file. The .proto file that defines the encoding of the VISS primary payload format is provided in the [[PAYLOAD ENCODING]] specification. A Protobuf compiler (e.g., protoc) is used to generate source code from the .proto file. This generated code facilitates the encoding and decoding between Protobuf and JSON payload formats. This code can be implemented in different languages, and is out of scope for the VISS standardization. An example implementation in the Go programming language can be found here.