This method represents the final step in the analysis of soil CEC by Methods 15B1, 15B2, 15B3 and 15C1. Ammonium ions displaced from exchange sites, together with NH4+ and Cl– derived from any NH4Cl solution residual in the extract, are measured simultaneously.
Ammonium is determined by an automated colorimetric procedure based principally on the methods of Henzell et al. (1968) and McLeod and Zarcinas (1976). The method employs the ammonium-phenate-hypochlorite reaction reviewed by Gehrke et al. (1968) and Searle (1984). In laboratories ill-equipped to handle phenol, the analytical finish for NH4+ used in Method 15I2 can be substituted. Chloride is determined colorimetrically, based on the reaction of Cl– with ferric nitrate and mercuric thiocyanate (McLeod and Zarcinas 1976).
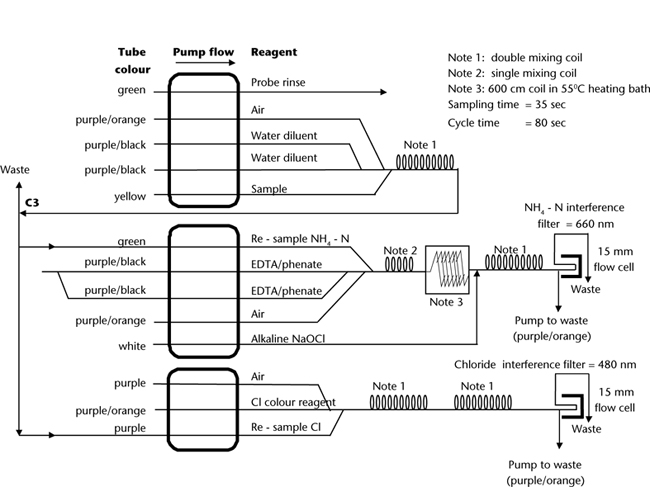
Method 7A2a, Gordon et al. (1993) and Section 4120 of APHA (2005) provide more details on SFA. One of the SFA technologies herein outlined is an example based on AutoAnalyzer I technology (Figure 15.8); the second utilises micro-bore technology (Figure 15.9). It is recognised, however, that improvements in system performance are ongoing, and incorporate a better understanding of the way in which dispersion, tubing diameter and flow rate are interrelated (Gordon et al. 1993). The analyst must be guided by the operational instructions and directions given by the manufacturer of their SFA equipment. This could require changes to the specified reagents and to the flow diagrams provided for this method.
Brij 35 Wetting Agent
As for Method 5A2a.
Figure 15.8. A continuous flow manifold (Auto Analyzer I technology) for CEC (NH4+ and Cl–).
Diluting Water (Water Diluent)
Deionised water containing 0.2 mL/L Brij Wetting Agent.
0.1 M Nitric Acid
Calcium-Potassium Nitrate-Nitric Wash Solution
Dissolve 150 g potassium nitrate (KNO3) and 60 g calcium nitrate [Ca(NO3)2.4H2O] in deionised water and make to 1 L. Take 600 mL of this solution and add 400 mL of 0.1 M HNO3 and make to 1 L. Chemicals for these solutions should be from the same batches used to prepare extracting solutions of Methods 15B1, 15B2, 15B3 or 15C1.
0.0162 M EDTA (disodium salt)
Dissolve 6.2 g disodium EDTA (C10H24N2Na2O8.2H2O) in deionised water and make volume to 1 L. Add 0.2 mL Brij 35 wetting agent.
Sodium Phenate Solution
Dissolve 11.25 g sodium hydroxide (NaOH) in approximately 250 mL deionised water and add, while hot, to 25 g phenol (C6H5OH; unstabilised). Cool and make to 1 L with deionised water.
Combined EDTA-Sodium Phenate Working Reagent
As required, combine 2 parts of 0.0162 M EDTA Solution with 1 part of Sodium Phenate Solution, mix well and filter if necessary.
2.5 M Sodium Hydroxide
Dissolve 100 g sodium hydroxide (NaOH) and make to 1 L with deionised water.
Alkaline Hypochlorite Solution
Mix equal volumes of sodium hypochlorite (NaOCl; ≈9–10% w/v free Cl2) and 2.5 M NaOH Solution. Prepare as required and filter immediately after preparation.
Saturation Mercuric Thiocyanate Solution
Prepare a saturated solution by shaking or stirring overnight about 0.75 g mercuric thiocyanate [Hg(CNS)2] with 1 L deionised water. Filter through a Whatman No. 44 paper. The solution is stable for a long period.
Ferric Nitrate Solution
Dissolve 20.2 g ferric nitrate [Fe(NO3)3.9H2O] in deionised water, add sufficient 14 M HNO3 until the solution becomes almost colourless (≈8 mL required), and dilute to 1 L with deionised water. Provided sufficient HNO3 has been added to prevent darkening, the solution should remain stable for a long period.
Chloride Colour Reagent
As required, mix equal volumes of saturated Hg(CNS)2 and Fe(NO3)3 Solutions and add 0.20 mL Brij 35 Wetting Agent to each litre.
As for Method 5A2a for Cl– part of the flow chart, and as for the NH4-N component of Method 7C2a, except that Reagent Water substitutes for the NaCl/H2SO4 Reagent. Use Ca-KNO-HNO3 Wash Solution described for Figure 15.8 Reagents for the probe rinse.
Figure 15.9. A micro-bore continuous flow manifold for CEC (NH4+ and Cl–).
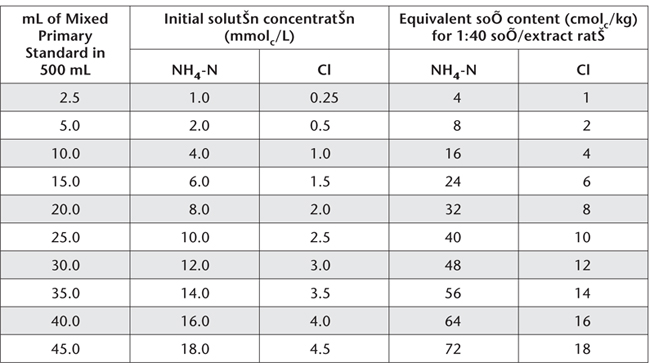
Table 15.17. Examples of dilutions and concentrations for NH4-N and Cl– Working Standards – CEC measurement.
Standard for Automated Determination of NH4+ and Cl–
Mixed Ammonium and Chloride Primary Standard
1 L contains 200 mmolcNH4-N and 50 mmolcCl–.
Dissolve 16.009 g ammonium nitrate (NH4NO3, previously dried at 100°C for 1 h) and 2.922 g sodium chloride (NaCl, previously dried at 105°C for 4 h), in Ca-KNO3-HNO3 Wash Solution, then make volume to 1 L with the same solution. Store in the dark in a plastic bottle.
Combined Ammonium and Chloride Working Standards
Dispense Mixed NH4 and Cl Primary Standard, as indicated in Table 15.17 into 500 mL volumetric flasks. Make to volume with Ca-KNO3-HNO3 Wash Solution from the same batch of reagents used for soil extraction.
Always avoid contact with fumes of NH3/NH4 and Cl2 in order to minimise analytical errors. Air used during continuous flow analysis of NH4-N and Cl– should be passed through dilute H2SO4 and AgNO3 solutions, respectively, to prevent possible contamination, particularly if room air quality cannot be guaranteed.
Ensure individual components of the CEC manifold for NH4-N and Cl– are connected as detailed in Figure 15.8 or Figure 15.9 (or as recommended by the manufacturer) and that Working Standards and soil CEC extracts are at room temperature before analysis. Prior to commencement of each batch, circulate reagents and Ca-KNO3-HNO3 wash solution for at least 20 min to ‘condition’ the system. Check instrument settings by pumping the highest working standard required for several minutes.
Determine concentration of NH4-N and Cl– in the soil extracts directly from regression equations or calibration curves derived from Working Standards (Table 15.17) run on commencement, after about every 30 CEC extracts, and on completion. A reagent blank should also be measured and adjustments made as necessary.
When shutting down the system, immediately transfer the pump tubes from the Ca-KNO3-HNO3 wash solution and the alkaline hypochlorite solution over to water wash. When these lines have been flushed of reagents, transfer all other pump tubes to water wash and continue pumping for at least 10 min.
As the soils are leached with 60% Aqueous Ethanol to remove most residual NH4Cl before NH4 ions are displaced, no correction for any free NH3 in the entrained NH4Cl Extracting Solution is required.
CEC[cmolc/kg] = [(NH4-Nmeasured – NH4-Nblank) – (Cl– measured – Cl– blank (all expressedascmol/kg)
Report CEC (cmolc/kg), expressed on an oven-dry basis. Use the air-dry moisture to oven-dry moisture ratio to convert to an oven-dry concentration. Refer to Method 2A1 for guidance with regard to this soil moisture calculation.
Table 15.17. Examples of dilutions and concentrations for NH4-N and Cl– Working Standards – CEC measurement.
