Concentrated salt solutions provide one alternative for the displacement of exchangeable bases and other cations from soils. Displacement, however, can be achieved at low solution ionic strength, provided the absorption affinity for soil colloids of the index cation selected is much larger than the absorption affinities of typical soil cations. Chhabra et al. (1975) demonstrated that the monovalent silver-thiourea complex (AgTU+) can serve this purpose. Subsequently, a single extraction method using unbuffered AgTU+ was found to be suitable for rapid determination of ECEC and exchangeable cations in soils dominated by low-activity clays with variable surface charges (Pleysier and Juo 1980). These researchers and Searle (1986) demonstrated that amounts of individual exchangeable bases extracted by both neutral NH4OAc and 0.01 M AgTU+ were usually highly correlated, although there can be differences. For example, Searle (1986) reported that NH4OAc could extract higher amounts of Ca2+ and Na+ in some soils. In contrast, 0.01 M AgTU+ appears able to extract more K+ than NH4OAc in soils containing interlayer K+ associated with vermiculite and partly weathered mica (Pleysier and Juo 1980). The reverse can also apply in other soils (Searle 1986).
This method is based on that reported by Blakemore et al. (1987). It involves equilibration of air-dry soil and 0.01 M AgTU+ for 16 h, with end-over-end shaking, followed by centrifugation and analysis of exchangeable bases. Sr2+ and Cs+ are included prior to analysis by AAS to prevent possible interferences from phosphate and ionisation, respectively. The residual extract is required for the determination of other ion exchange properties. As highly weathered soils of low ionic strength (e.g. I <0.01) usually contain low levels of salinity, there is no provision for removal of soluble salts.
0.01 M AgTU+
Dissolve 150 g thiourea [CS(NH2)2] in about 3 L deionised water in a 10 L container. Slowly add 5 L of deionised water containing 16.987 g silver nitrate (AgNO3) while stirring with a magnetic stirrer. Make volume to 10 L with deionised water.
Strontium Chloride/Caesium Chloride Solutions (only required if using an AAS analytical finish)
Stock Sr/Cs Solution
1 L contains 7.5 g Sr2+ and 25 g Cs+.
Dissolve 46 g strontium chloride (SrCl2.6H2O) and 63.6 g caesium chloride (CsCl) and dilute to 2 L with deionised water. Store in a plastic or borosilicate bottle.
1+3 Sr/Cs Diluting Solution
Dilute 106 mL Stock Sr/Cs solution to 1 L with deionised water. Store in plastic or borosilicate bottle.
1+9 Sr/Cs/AgTU Diluting Solution
Dilute 89 mL Stock Sr/Cs solution and 167 mL 0.01 M AgTU+ to 1 L with deionised water. Store in plastic or borosilicate bottle.
Caesium Chloride Solution
1 L contains 1.0 g of Cs+.
Dissolve 1.267 g caesium chloride (CsCl) and dilute to 1 L with deionised water. Store in plastic or borosilicate bottle.
Saturated Potassium Chloride
Add approximately 180 g potassium chloride (KCl) to 500 mL deionised water and mix well.
Mixed Primary and Secondary Standards for Ca2+, Mg2+, Na+ and K+
As for Method 15A1.
Table 15.14. Examples of dilutions and concentrations for Ca2+ and Mg2+ Working Standards – 0.01 M AgTU+.
|
|
Equivalent soil content (cmolc/kg) of Ca & (final) following: |
|
mL of Secondary Standard in 500 mL |
Initial solution concentration (mmolcCa & Mg/L) |
1 + 3 dilution* of samples only |
1 + 9 dilution† of samples only |
Mixed Ca & Mg Secondary Standard (10 mmolcCa & Mg/L) |
|||
0.5 |
0.01 |
0.2 |
0.5 |
1.0 |
0.02 |
0.4 |
1.0 |
2.5 |
0.05 |
1.0 |
2.5 |
5.0 |
0.10 |
2.0 |
5.0 |
7.5 |
0.15 |
3.0 |
7.5 |
12.5 |
0.25 |
5.0 |
12.5 |
25.0 |
0.50 |
10.0 |
25.0 |
40.0 |
0.80 |
16.0 |
40.0 |
*Accurately dilute sample extracts only with 1+3 Sr/Cs Diluting Solution if analysing by AAS. For ICPAES, substitute the 1+3 Sr/Cs Diluting Solution with 0.01 M AgTU+ Extracting Solution.
†AAS analysis requires accurate dilution of sample extracts only with 1+9 Sr/Cs AgTU+ Diluting Solution. For ICPAES analysis, substitute this Sr/Cs Diluting Solution with 0.01 M AgTU+ Extracting Solution.
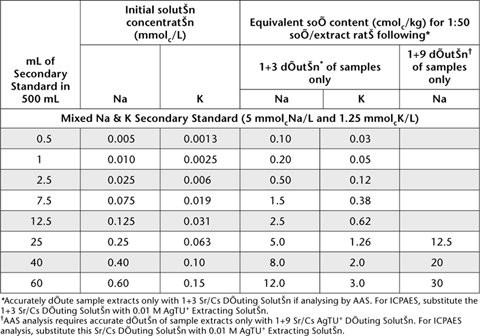
Accurately dispense Mixed Ca2+ and Mg2+ Secondary Standards of required concentrations as indicated in Table 15.14 and Mixed Na+ and K+ Secondary Standards of required concentrations as indicated in Table 15.15 into 500 mL volumetric flasks. Add 125 mL 0.01 M AgTU+ and (if required for AAS analysis) 40 mL Stock Sr/Cs solution, mix well, and make to volume with deionised water. Store these solutions in the dark and discard should any precipitate develop with time.
Weigh 1.00 g of air-dry soil (<2 mm) into an 80 mL polypropylene centrifuge tube. Add 50.0 mL of 0.01 M AgTU+, stopper securely and mechanically shake end-over-end at ≈25°C for 16 h (overnight). Centrifuge until a clear supernatant is obtained.
Accurately dilute a portion of the sample supernatants only, either 1+3 or 1+9 with 1+3 Sr/Cs Diluting Solution (if analysing by AAS) or 1+9 Sr/Cs AgTU+ Diluting Solution (if analysing by ICPAES). Include a method blank throughout and retain for measurement of exchangeable bases.
As for Method 15A1 but using relevant instruments, standards, diluting solutions and blanks. Report exchangeable Ca2+, Mg2+, Na+ and K+ (cmolc/kg), expressed on an oven-dry basis. Use the air-dry moisture to oven-dry moisture ratio to convert to an oven-dry concentration. Refer to Method 2A1 for guidance with regard to this soil moisture calculation.
Table 15.15. Examples of dilutions and concentrations for Na+ and K+ Working Standards – 0.01 M AgTU+.