This method is similar to 15A1 except that there is a pre-treatment with aqueous ethanol and aqueous glycerol to remove soluble salts. This pre-treatment is desirable when soil EC (1:5 soil/water; Method 3A1) exceeds ≈0.3 dS/m.
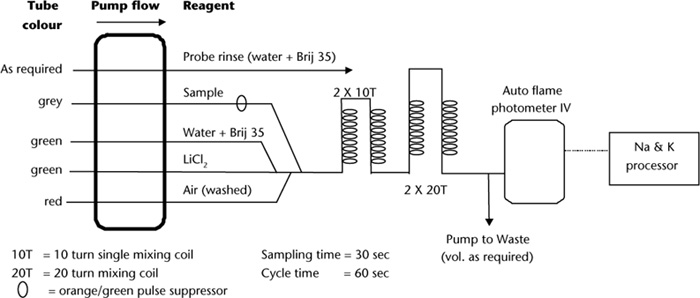
Figure 15.2. Continuous segmented flow manifold for Na+ and K+ in 1 M NH4Cl soil extracts.
The effectiveness of various solvents for removal of soluble salts has been discussed by Tucker (1985). Here, aqueous ethanol and aqueous glycerol, at the soil solution ratio and extraction time of this method, can remove 0.6–0.7% of finely divided gypsum from soil. If more is present or the gypsum resists dissolution, direct measurement of gypsum and other soluble salts are recommended, followed by appropriate adjustments to exchangeable bases.
60% Aqueous Ethanol (w/w)
Mix 665 mL of 96% ethanol (C2H5OH; e.g. special grade Sarina – SMF3; S.G. 0.803) and make to 1 L with deionised water. Deionise if EC >10-3 dS/m or if pH is not within the range 5.5–7.0. Pass through a column of fresh, mixed-bed ion exchanger in the H+/OH– form, such as Zeo-Karb 225/De Acidite FF or equivalents.
Remove dissolved air by boiling or by drawing the prepared reagent through a fine jet under vacuum into a Buchner filtration flask connected through a trap to a vacuum pump.
20% Aqueous Glycerol
Combine 200 mL 87–88% technical glycerol (CH2OH.CHOH.CH2OH; wt/mL about 1.23 g) with 800 mL deionised water. Deionise if necessary as described for 60% Aqueous Ethanol. Boil to sterilise and add 0.5 g of thymol crystals (C10H14O) as a preservative.
Weigh 5.00 g air-dry soil (<2 mm) into a preweighed 50 mL centrifuge tube and add 25 mL 60% Aqueous Ethanol. Seal and shake for 30 min. Within 30 min of that action, centrifuge and remove the supernatant solution by suction.
Drain the tube upside down on a piece of absorbent paper to remove excess solvent. Disperse the soil mechanically and add a second 25 mL of aqueous ethanol, centrifuge and decant and drain as before. Repeat the process a third time using 20% Aqueous Glycerol in place of Aqueous Ethanol. Weigh the centrifuge tube to determine the approximate volume of entrained aqueous solvents. Transfer the pretreated soil to a 250 mL plastic extracting bottle using 100 mL 1 M NH4Cl at pH 7.0 Extracting Solution. Proceed with the extraction and analysis of the exchangeable basic cations as described in Method 15A1.
When 5.0 g of soil are extracted with 100 mL of NH4Cl, increase the determined values by the ratio {[100 + Mass (g) of entrained aqueous solvent]/100} to obtain the concentration of exchangeable bases on an air-dry basis.
Report exchangeable Ca2+, Mg2+, Na+ and K+ (cmolc/kg), expressed on an oven-dry soil basis. Use the air-dry moisture to oven-dry moisture ratio to make the oven-dry conversion. Refer to Method 2A1 for guidance with regard to this soil moisture calculation.