The soil extraction component of this method, including conditions of storage of filtered and unfiltered 2 M KCl soil extracts, is identical to that of Method 7C1. Mineral-N fractions in the clarified soil extract are then determined by automated colorimetric procedures. SFA systems typically run faster than similar FIA systems operating at high sensitivity.
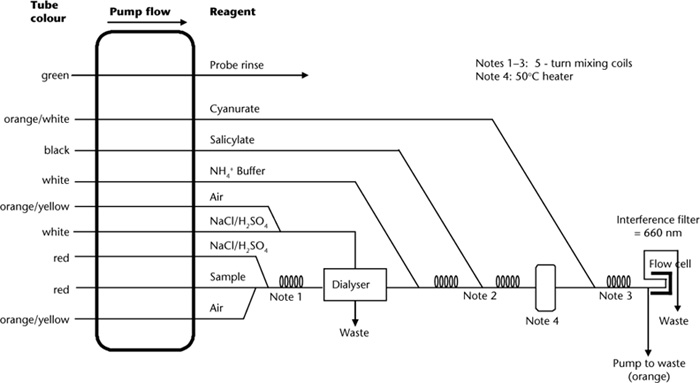
Ammonium ions are measured by a modified Berthelot indophenol reaction (Searle 1984) similar to that of Method 7A2a. Ammonia reacts with hypochlorite ions that are generated in situ by alkaline hydrolysis of sodium dichloroisocyanurate. The monochloramine formed then reacts with salicylate ions in the presence of sodium nitroprusside to form a blue indophenol-type compound that absorbs strongly at 660 nm. A citrate buffer is employed to chelate metals that would otherwise form insoluble hydroxides or carbonates.
In the NO3-N procedure, NO3– is reduced to NO2– by hydrazine in the presence of CuSO4 in a buffered alkaline solution at 45°C, and the NO2– produced, along with any NO2– already present in the soil extract, is determined by a modified Griess-Ilosay method (Best 1976). A description of this reaction is contained in the general review of the determination of inorganic forms of N given by Mulvaney (1996).
The analytical finish, with extended range detectors, is capable of analysing up to 100 mg/kg of N as NH4 and NO3-N in undiluted extracts. Since levels of NO2-N are normally insignificant in agricultural soils, it is usual to express NO3-N + NO2-N as NO3-N, although these can be expressed separately if necessary.
2 M KCl Extracting Solution
As for Method 7C1. Ensure any stored solution is well stoppered to prevent NH3 absorption from the environment.
Reagent Water (Water)
Deionised or distilled water, analytically free of NH3/NH4+ and other anions of interest, and containing no particles >0.20 μm.
Brij 35 Wetting Agent
As for Method 5A2.
Wash Solution for Analyser (Probe Rinse)
Add 1 mL Brij 35 Wetting Agent to each 1.0 L of 2 M KCl Extracting solution – same batch as used for the unknown samples.
Ammonium-N Reagents
NH4+ Buffer Solution
Dissolve 14.2 g of anhydrous disodium hydrogen orthophosphate (Na2HPO4) in 900 mL Reagent Water in a 1.0 L Schott bottle. Add and dissolve 50.0 g sodium potassium tartrate (KNaC4H4O4.4H2O), then 48.2 g sodium hydroxide (NaOH), mix well and make volume to 1.0 L with Reagent Water after adding 1 mL Brij 35 Wetting Agent. Store at ≈4°C.
Salicylate Reagent
Weigh 112 g of sodium salicylate (C6H4(OH)COONa), transfer into a 2 L Schott Bottle and dissolve in ≈900 mL Reagent Water. Weigh 0.8 g of sodium nitroprusside dihydrate {Na2[Fe(CN)5NO].2H2O} into a beaker and dissolve in ≈900 mL Reagent Water. Combine the sodium nitroprusside solution with the sodium salicylate solution and make volume to 2 L with Reagent Water. Store at ≈4°C.
Cyanurate Reagent
Weigh 10 g sodium-3,5-dichloro-S-triazine-2,4,6-trione (C3HCl2N2O3.Na) and transfer to a 2 L Schott Bottle. Separately weigh 23 g sodium hydroxide (NaOH) and dissolve in Reagent Water. Combine and mix and make to 2.0 L with Reagent Water. Commercial grade chemicals are satisfactory. The active chemical in this reagent is also called sodium dichloroisocyanurate. Store at ≈4°C.
Dialyser Diluent and Pick-up Solution (NaCl/H2SO4)
Dissolve 100 g sodium chloride (NaCl) in 900 mL of Reagent Water in a 1.0 L Schott Bottle. Add 7.5 mL 18 M H2SO4, mix then add 1.0 mL Brij 35 Wetting Agent and make to 1.0 L with Reagent Water.
Nitrate-N Reagents
Stock Tartrate/Copper Solution
Dissolve 26.9 g sodium potassium tartrate tetrahydrate (KNaC4H6.4H2O) in around 900 mL Reagent Water. Next predissolve and add 1.8 g copper sulfate (CuSO4.5H2O), mix well and make to 1.0 L. Store in a borosilicate flask at ≈4°C.
Alum – Sodium Chloride Stock Solution
Weigh 100 g potassium aluminium sulfate [Alum; KAl(SO4)2.12H2O] and transfer to a 1 L Schott Bottle.
Add 100 g sodium chloride (NaCl) then dissolve in Reagent Water and make to 1.0 L. Store in a borosilicate flask at ≈4°C.
Stock Copper Sulfate Solution
Dissolve 1.2 g of copper sulfate (CuSO4.5H2O) in 100 mL of Reagent Water.
Working Alum–Sodium Chloride Solution (Alum)
Dilute 50 mL of Alum–Sodium Chloride Stock Solution to 1.0 L with Reagent Water (measuring cylinder accuracy) and mix well.
Dialyser Pick-up Solution (Recipient for NO3–)
Add 10 mL of Stock Tartrate/Copper Solution to a 1.0 L Schott Bottle. Add 1 mL Brij 35 Wetting Agent, mix and make to 1.0 L with Reagent Water.
Hydrazine Solution
Dissolve 1.3 g hydrazine sulfate (NH2-NH2-H2SO4) in about 900 mL Reagent Water, add 1.3 mL Stock Copper Sulfate Solution, mix well and make volume to 1.0 L. This solution is stable for at least 1 month, particularly if stored in a borosilicate flask at ≈4°C.
Nitrate Buffer
Separately weigh and dissolve 22.5 g sodium tetraborate (Na2B4O7.10H2O) and 2.5 g sodium hydroxide (NaOH) in deionised water, mix well and make to 1.0 L with Reagent Water. This solution is stable for at least one week, particularly if stored in a borosilicate flask at ≈4°C.
Sulfanilamide Colour Reagent
Dilute 50 mL ortho phosphoric acid (H3PO4; sg. 1.75) in about 75 mL Reagent Water in a 500 mL flask. Weigh, dissolve completely in Reagent Water and add 5.0 g LR sulfanilamide (C6H8N2SO2). Next weigh, dissolve (Reagent Water) and add 0.25 g N-1-napthylene diammonium dihydrochloride (C12H16Cl2N2). Mix well and make to 500 mL with Reagent Water. Store in a borosilicate flask at ≈4°C and discard if a pink coloration appears.
Ammonium and Nitrate Standard Solutions
Ammonium Primary Standard
1 mL contains 0.20 mg of NH4-N.
Dissolve 0.4717 g ammonium sulfate [(NH4)2SO4; previously dried at 100°C for 4 h] in 2 M KCl Extracting Solution and make volume to 500 mL. Add several drops of chloroform (CHCl3) to extend shelf life. Solution can be held in borosilicate glass for at least 6 months if stored at ≈4°C.
Nitrate Primary Standard
1 mL contains 0.50 mg of NO3-N.
Dissolve 1.8046 g potassium nitrate (KNO3; previously dried at 105°C for 4 h) in 2 M KCl Extracting Solution and make to 500 mL in a volumetric flask. Preserve with several drops of chloroform (CHCl3). This solution is stable for at least 6 months if stored in a stoppered borosilicate bottle at ≈4°C.
Ammonium and Nitrate Combined Secondary Standard
1 mL contains 0.05 mg of NH4-N and 0.05 mg of NO3-N.
Pipette 125 mL of NH4+ Primary Standard and 50 mL of NO3– Primary Standard into a 500 mL volumetric flask and make to volume with 2 M KCl Extracting Solution. Freshly prepare when working standards are required.
Ammonium and Nitrate Combined Working Standards
Pipette 0, 1.6, 3.2, 4.8, 8.0, 12.0, 16.0, 24.0, 32.0, 40.0 and 60.0 mL NH4+ and NO3– Combined Secondary Standards into separate 200 mL volumetric flasks. Make to volume with 2 M KCl extracting solution. These solutions contain 0, 0.4, 0.8, 1.2 … 15.0 mg N/L in both NH4 and NO3 forms, equivalent to soil concentrations of 0, 4, 8, 12 … 150 mg NH4-N/kg and 0, 4, 8, 12 … 150 mg NO3-N/kg for a soil/solution ratio of 1:10.
Extract soils and prepare clarified 2 M KCl extracts as for Method 7C1.
Set up the automated colour, continuous segmented flow autoanalysis equipment as recommended by the manufacturer of the equipment: refer to Figures 7.10 and 7.11 for examples based on microbore technology.
‘Condition’ the manifolds before use, make a final check on instrument settings, then determine N concentrations in 2 M KCl extracts from relevant Working Standards run on commencement and as required throughout the batch. Dilute soil extracts with 2 M KCl extracting solution if N concentrations exceed the top standard. Also use 2 M KCl as the wash solution during autoanalysis.
The result from the NO3– part of the manifold represents NO3-N + NO2-N. When NO2– is known or assumed to be absent or insignificant, however, report as NH4-N and NO3-N (mg N/kg).
If conditions given for Method 7C1h apply and NO2-N is known to be present, operate the system as earlier described but substitute deionised water for the Hydrazine Sulfate Solution in the NO3 segment of the manifold and for all reagents in the NH4 segment. Use a selection of NO2 working standards and record NO2-N concentrations.
NO3-N (air dry) = {[NO3 + NO2-N] – NO2-N}
Report NO3-N (oven-dry). Use the air-dry moisture to oven-dry moisture ratio to make the oven-dry conversion. Refer to Method 2A1 for guidance with regard to this soil moisture calculation.
No calculation necessary, as NO2-N concentration is zero.
Report NH4-N and NO3-N (mg N/kg) on an oven-dry basis. Use the air-dry moisture to oven-dry moisture ratio to make the oven-dry conversion. Refer to Method 2A1 for guidance with regard to this soil moisture calculation.
Figure 7.10. A micro-bore continuous flow manifold for KCl-extractable ammonium-N.
Figure 7.11. A micro-bore continuous flow manifold for KCl-extractable nitrate-N.