This method guided by Moody and Cong (2008) uses 0.033 M KMnO4. It targets labile or active SOC, including any WSOC that might be present. Results typically correlate with several key soil properties: aggregate stability (Blair et al. 1995, 1996; Bell et al. 1999); ECEC and pH buffer capacity (Moody et al. 1997); and microbial biomass-C (Moody et al. 1999). Across a range of soils, PPOC is generally well correlated with TOC (e.g. Moody et al. 1997). At least portion of the measured PPOC, however, can sometimes be the result of short-term land management practices that add highly labile WSOC to the ‘system’ (sucrose is an example). Elevated BOD in adjacent natural waters can result if this WSOC leaves the site in runoff (Rayment 2003).
An earlier method of oxidising SOC by permanganate (Loginow et al. 1987) used 0.333 M, 0.167 M, and 0.033 M KMnO4 to differentiate three fractions whereas Weil et al. (2003) preferred 0.02 M KMnO4 as the oxidising agent. The inclusion of CaCl2 in the reagent is to enhance flocculation of the soil extracts. Reaction time is precisely 2 min plus precisely 5 min of subsequent standing/settling time.
Reagent Water
As for Method 6A1.
Dissolve 14.7 g calcium chloride dihydrate (CaCl2.2H2O) and make to 1.0 L with Reagent Water.
0.033 M Potassium Permanganate
Dissolve 5.2151 g analytical grade potassium permanganate (KMnO4) in Reagent Water in a small beaker with stirring and heating (use a hotplate no warmer than 60°C) until fully dissolved. Filter through a funnel containing a plug of washed borosilicate glass wool and dilute to 1.0 L in a volumetric flask. Store the solution in an amber glass bottle or in the dark.
Standard Potassium Hydrogen Phthalate Solution (0.0405 M)
1 mL contains 4.504 mg of C.
Weigh and dissolve 9.5728 g potassium hydrogen phthalate (KHC8H4O4; previously dried for 2 h at 110°C) and make volume to 1.0 L with Reagent Water. (This C-standard is only required for double-checking purposes.)
Working Standard Solutions
Whether testing in the laboratory or in the field, prepare five Working Standard Solutions from the same batch of 0.033 M KMnO4, Reagent Water and 0.1 M CaCl2 as outlined below. For Working Standards 1, 2, 3, 4 and 5, accurately add 20, 15, 10, 5 and 0 (zero) mL of Reagent Water, then dispense sequentially and accurately into the same flasks 5.0, 10.0, 15.0, 20.0 and 25.0 mL of 0.033 M KMnO4 (same batch as to be used for the unknowns) and mix well. The molarities of KMnO4 in these Working Standards equate to 6.6, 13.2, 19.8, 26.4 and 33 mM KMnO4, respectively. Next add 1.0 mL of 0.1 M CaCl2 to each standard solution and mix well.
Add 1.0 mL of each of the five Working Standard Solutions to a set of numbered, 50 mL calibrated plastic tubes and add Reagent Water to the 50 mL mark. Cap and shake by hand. Prepare these Working Standard Solutions on the day of use. If for field use, take to the field already prepared.
Combine and mix soil sub-samples and then air dry a thin layer of each soil sample in the sun for 1 h in a dust-free place. After this drying step, crush and remix the sample, ideally to a particle size of <2 mm.
At a similar time, set up a portable colorimeter (e.g. a palm-top Hach® colorimeter able to measure absorbance at 550 nm) for later use.
Weigh 5.0 g of the field-dried soil (or use a suitable scoop equivalent to 5 g soil) into a 50 mL plastic centrifuge tube, noting that weight/volume relationships can vary with soil type, and whether recently cultivated or otherwise. Into each tube dispense accurately 25.0 mL of 0.033 M KMnO4 solution then add 1 mL of 0.1 M CaCl2 solution to assist flocculation of soil particles. Cap the tube then shake the mixture by hand for precisely 2 min. Leave the mixture to stand for precisely 5 min, then immediately take 1 mL of the supernatant using a pipette and dilute this aliquot in a plastic centrifuge tube to the 50 mL mark with Reagent Water (or water known to be free of dissolved OC).
Zero the portable colorimeter (or spectrophotometer) with Reagent Water and measure the absorbances of all standard solutions and samples at a wavelength of 550 nm (see Note 1). Plot mM KMnO4 of the five Working Standards (x-axis) against absorbance (y-axis) and either draw a straight line through the points or fit a regression line to the relationship. Use this relationship to determine the concentration of KMnO4 (mM) left in the unknown samples after the oxidation period.
As an occasional check on the quality of reagents, particularly 0.033 M KMnO4, dispense (say) 1 mL and 2 mL of Standard Potassium Hydrogen Phthalate Solution into the 50 mL plastic centrifuge tubes normally used for unknown soil samples. Evaporate the dispensed standard solutions to dryness in an oven, at not greater than 65°C, then cool to room temperature before dispensing accurately 25.0 mL of 0.033 M KMnO4 solution, adding 1 mL of 0.1 M CaCl2 and continuing as previously described. These should contain 4.504 and 9.008 mg of C, respectively. If not the case, double-check the quality of the KMnO4 solution.
When performed in the laboratory, the soil samples should arrive as quickly as possible following field sampling or otherwise kept at or below 4°C during transportation in order to suppress biological activity prior to efficient air drying at 40°C.
After drying, crush, grind or sieve the soils to <0.5 mm, then weigh 5.0 ± 0.1 g and proceed as described for the field procedure. Expect laboratory-performed tests to be slightly higher in PPOC and also more precise than for corresponding soils analysed in the field.
Use the following equation to calculate PPOC with units of g C/kg. This is based on the assumption that each 1.0 mM of MnO4– consumed in reducing Mn7+ to Mn2+ is equivalent to the oxidation of 0.75 mM of C (or 9.008 mg of C). The following equation takes this and the soil/solution ratio into account:
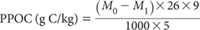
where:
M0 = initial concentration of KMnO4 (0.033 M = 33 mM)
M1 = concentration of KMnO4 (mM) after oxidation (calculated from standard calibration curve)
Report PPOC (g C/kg) on an air-dry basis.
1. If the absorbance of any sample is less than 0.4, repeat the extraction using 2.5 g of soil instead of 5 g of soil, to ensure excess KMnO4 is present throughout the reaction.